…as Guyana builds oil & gas capacity to rival Trinidad & Tobago
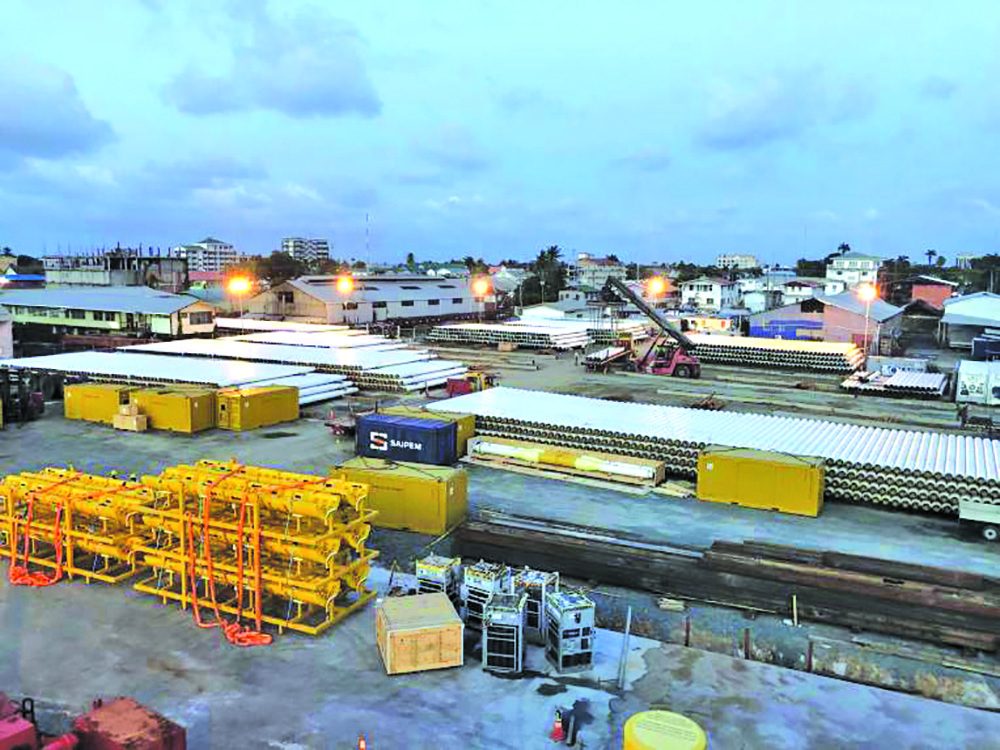
ExxonMobil, which has largely sourced services from neighbouring Trinidad and Tobago for its operations in Guyana since it started exploration activities here, said that with the strides Guyana has made to build capacity, these services are likely to be sourced locally by 2022.
Exxon’s Country Manager Alastair Routledge recently spoke of this in another section of the media, where he said that Guyana has undergone drastic changes in its oil and gas capacity since the early days when the company made its first oil discovery in the Stabroek Block in 2015.
He had said that when Exxon started exploration there was no infrastructure or expertise in place locally to support the company’s operations. This had led Exxon to source these services from Trinidad and Tobago, which has been producing oil on a commercial basis since 1908.
According to Routledge, however, it is anticipated that this supply chain will have been moved from Trinidad to Guyana by next year so that these services can be accessed locally. When this publication contacted Public and Governance Affairs Advisor at Exxon, Janelle Persaud, she noted that a number of Exxon’s prime contractors have been expanding their services from Trinidad into Guyana.
“When we started operations most of the prime contractors were operating out of Trinidad… and they have steadily been moving those services into Guyana… and what Alastair is saying is that we hope to have moved all of those into Guyana in 2022,” she said.

Alastair Routledge
Among these prime contractors are Halliburton – a United States (US)-based oilfield contractor that has been providing a range of drilling services to Exxon, Saipem – which has been providing installation services for Exxon’s Liza Phase 2 and TechnipFMC, which is in charge of installing the subsea system for the Payara oil field – Exxon’s third development in Guyana’s water.
Esso Exploration and Production Guyana Limited (EEPGL), Exxon’s local subsidiary, is the operator and holds 45 per cent interest in the Stabroek Block, while Hess Guyana Exploration Ltd holds 30 per cent interest and CNOOC Petroleum Guyana Limited, a wholly-owned subsidiary of CNOOC Limited, holds the remaining 25 per cent interest.